Telematics Gateway Powering a Personalized In-Vehicle Experience
“Automotive Data is now more profitable than the car itself”
The Connected Car revolution has been the key trend in the automotive industry and has transformed the path ahead for Automotive OEM’s across the globe. Technologies such as ADAS, Self-driving, Connected Car, and Fleet Management have been powering the transformation in the automotive industry. Research by Markets and Markets estimates the connected vehicle market at 166 Billion USD by the year 2025 and is bound to be growing.
The digital transformation of the human mind has brought about a great change in the way we live, the way we travel, and the way we consume experiences across verticals. Transformation in the automotive sector such as shared mobility, extensive navigation systems, predictive maintenance of vehicles has laid the roadblocks for extensive amounts of data from the car transforming the commercial models of the automotive industry.
Why Personalisation in the Car
Organizations across verticals are now focusing on increasing customer loyalty and net promoter score amongst customers. According to a study by Bain & Company, increasing customer retention rates by just 5% can increase profits by 25% to 95% for an organization. Personalized in-vehicle experiences can be the way forward for automotive companies to build loyalty and increased customer retention through a pathway of personalized customer relationships. With consumers now experiencing personalization in their homes and offices through Alexa, Echo, and the other SmartHome players, it would be the right time to extend this personalization onto the mobility sector.
Indian spend 7% of each day commuting to the office, Americans spend 10 hours and 50 minutes per week and this time continues to rise across countries.
This valuable time provides automotive OEM and the platform companies significant data and provision to provide custom experiences and would serve as a key differentiator for the manufacturers.
There are various examples of how data can transform the personalized experience for vehicle owners :
1. Pre-ordered breakfast ready for takeaway at your favorite restaurant en route to your office
2. Predictive maintenance of the batteries, automated scheduling of maintenance and service requests with the retailer based on the health of the vehicle
3. Connected workplace within the vehicle – Wi-Fi hotspot and video conferencing while on travel
Challenges and The Eco-System Required to Drive Personalisation
The ability to power a personalized in-vehicle experience cannot be taken up by a single entity such as the OEM or the Telecom Operator or the Service Provider. There are various challenges in the road to providing such experiences within the vehicle.
Harnessing and Collecting Data: Automotive manufacturers do not manufacture cars with a data-centric approach. There is now a need to collect the data from vehicles and store and maintain the data. 25GB of data is generated per hour per vehicle on average, there has to be a well-defined strategy on the data layer and good synergy between the telematics gateway manufacturer and the IoT platform would lay the foundation for a successful digital mobility experience.
Effective Value and Use of the Data: Effective utilization of the data available and effective strategy to build across the algorithms and analytics layer is a must. The data must be available across platforms, services, departments, and after-market players. Also, the design and development of such analytics should be a well laid out strategy since some decisions might have to be taken on the edge and some on the cloud.
Integration, Security, and Life-Cycle: Data Security and the maintenance of the services would be a key step in ensuring the success of such an experience. Automotive retailers and aftermarket service providers, being the face of the OEM to consumers will have to take care of the integration and life-cycle of such offerings.
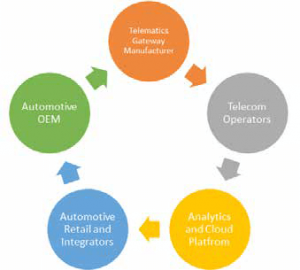
For the connected car revolution and bringing about an effective mobility experience, there needs to be an effective synergy between 5 different stakeholders:
1. Telematic Gateways and Device Manufacturer: The telematics gateway manufacture is responsible for an effective and modular gateway to connect to various vehicles and effective product development in pipeline complementing the Automotive OEM’s.
2. Telecom Operators: The vehicles and the gateways need to be connected to the various data networks across the globe. Telecom operators providing the embedded connectivity for such connected applications also need to take care of SIM Management and associated data privacy and security layers.
3. Analytics and Cloud Platform: Automotive OEM and other stakeholders in the ecosystem lack the experience to manage the vast amounts of data and device the right strategy for the maintenance of such data. Building an agile and scalable framework for various applications and corresponding the AI algorithms to be run on the cloud need to be taken care by the IT providers and Cloud infrastructure companies.
4. Automotive Retail Integrators: Providing aftermarket services such as fleet management, service, and maintenance scheduling and other applications are driven by integrators who put together the device, cloud, and analytics while also taking care of the integration of the gateways onto the vehicles. The integrators are the first face to end consumers and play a vital role in the whole eco-systems
5. Automotive OEM: Vehicle Manufacturers and the OEM’s need to work in tandem with other stakeholders to ensure that the gateways are able to effectively communicate with the ECU and the right protocols. The manufacturers and the integrators need to be work together to position a single brand image and purpose since they will always be linked to each other.
Therefore, for a successful connected mobility experience, there needs to be an active synergy between the 5 stake-holders and bring about a change in the auto value-chain.
Telematics Gateway and Personalisation
The telematics gateway will be positioned as the heart of the whole connected mobility transformation. Bridging the ECU Data to the cloud, the protocol conversion, the data storage, sensor-based edge analytic, and other important features need to be taken care of by the Telematics Unit on the vehicle. With V2X and V2V communication in the near future, a single secure gateway is needed on the vehicle ensuring scalability and accessibility.
Vehicles are increasingly dependent on electronic control units (ECU) to manage the advanced features that enhance the driving experience. The telematics gateway functions as a bridge to the ECU used by these different applications, managing different protocols such as GMLAN / SAE 1939 / 71 / ISO 1576-5 and the external interfaces such as Ethernet / HS CAN / LS CAN and CAN FD.
The Telematics gateway also encompasses sensors that can enable applications such as E-Call / Driver behavior analysis / Idling time and other key features that can enhance the personalization experience. With the embedded connectivity on the Telematics Unit, there can also be an effective network hotspot within the car for the passengers to access the Internet and work while in the car. The Bluetooth and Wi-Fi connectivity can also provide for an interface to connect to the various sensors such as the fuel sensor, tire pressure, door sensors enabling a single gateway for all data points within the vehicle.
Complementing the telematics gateway with Machine Learning and AI Analytics, Automotive OEM can redefine their value creation model to a more data-centric approach
Key Considerations on the Telematics Gateway and the Future
With Telematic Gateways playing a crucial role in connected mobility, there are a few key aspects to be considered when choosing a gateway for the connected mobility transformation.
Vehicle Interfaces and Protocols
With various interfaces available across the range of vehicles such as CAN / Ethernet, J1939, and many others. Telematic Gateways should be modular in architecture to suit the complete available range. Ethernet is available in vehicles to connect to the infotainment systems and the IP Cameras on the vehicle, J1939 being support in the heavy-duty vehicles such as trucks and tractors and CAN being the backbone of various electronics systems within a car; each network has individual application within the connected mobility ecosystem. To extend the connected mobility ecosystem, it is important for the Telematics Gateway to be able to connect to various networks to harness available data providing an extensive transformation experience.
Another key aspect to consider is the software stacks available on the TCU. With protocols such as GMLAN on the LS CAN Interface, ISO5765-4 on the HS CAN Interface, CANOpen and the list keeps growing. A scalable software on the gateway is a must to ensure interoperability and reduced development time for customized applications. With secure and scalable software on the gateway, Automotive OEM and integrators can be assured of one multi-purpose gateway catering to various vehicles and mobility infrastructure.
Connectivity
Another key aspect to be taken care of is the ability of the Telematics Unit to be able to scale up and down the communication based on the requirement and connectivity infrastructure. With networks such as NBIoT, 5G, Wi-Fi 6.0, and DSRC (Dedicated Short Range Communication), the Telematics Gateway should be able to integrate with various wireless infrastructure based on the end application.
There needs to be an ideal compromise between the connectivity options, input interfaces, form factor of the gateway, and the price to the position as an ideal gateway for the connected mobility transformation.
Conclusion and the Next Steps Ahead
With connected mobility being a huge ocean and the need for the automotive manufacturers to scale up the value chain while focusing on a more data-centric commercial model, there are a few key questions to be answered while stepping into the telematics and personalization experience.
1. What is the drive experience we aim to provide to complement our connected car?
2. How do we manage the huge amounts of data? Who owns the data? What is the best use of the data?
3. What is the right IoT Platform to build analytics and algorithms and who are the right ecosystem partners?
4. How do we monetize the personalization experience?
5. How do we offer the personalised experience to end customer?