Embedded Telematics: Unlocked
Isn’t it amazing how versatile today’s embedded systems are? From industrial, automotive, medical to AI, there is no such field where embedded systems have touched and not reaped wonders. Indeed, the impact is more so prominent in the world of “Vehicle Telematics.”
Vehicle Telematics is the technology that helps to “be connected” with your vehicle anytime, anywhere.
Besides tracking and navigation, telematics enables users to get precise details about engine performance and even the component failures, minimize downtime with predictive maintenance, and score driving habits to ensure individual and road safety. The telematics system assures safety by alerting owners about imminent threats and in case of emergency, the system works efficiently to summon timely road assistance and reduce fatalities.
Wondering how all of these are realized in a vehicle? It is the collective effort of various electronics in the vehicle, in particular, the “Telematics Control Unit (TCU)”
At iWavesystems, a leading embedded solution provider company, we have what it needs to enable intelligent telematics solutions. Our expertise in turnkey embedded solutions involving hardware, software, security, OTA makes iWave a preferred choice of OEMs for leading-edge automotive applications.
Why TCU?
Today all modern cars are implanted with sensors that monitor every minute details of the vehicle – sensors to gauge air temperature, fuel pressure, engine vibration, fuel consumption, crash detection, etc.
However, no amount of data is useful unless there is an integrated electronic system to analyze and make use of the generated data. This is achieved with the help of ECUs (Electronic Control Unit). Depending on the make and model of the vehicle, there can be as many as 70-80 integrated ECUs managing various operations in a vehicle. Examples: engine control unit, cruise control unit, door control unit, etc.
ECUs collect data from sensors, process it, and ensure efficient operation of the vehicle system. But the data accumulated by ECU is restricted for access within the vehicle. A mechanic can analyze the ECU data by plugging in his PC/diagnostic tool into the vehicle. This gives information regarding the working status of sensors and other components and helps to detect faults precisely. Often, the user has no idea of what’s going on inside the vehicle and ends up not knowing what to do in case of an emergency.
What if this data needs to be accessible to the user?
The solution is accomplished with the help of The TCU (Telematics Control Unit).
TCU: The heart of telematics
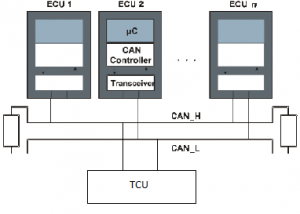
The TCU is a highly integrated system that captures data from the ECUs, then interprets it and relays the information to the user, via the cloud. This is achieved with the help of the Controller Area Network (CAN-bus), a robust and reliable communication protocol used for the transfer of data between multiple electronic components of a vehicle e.g. sensors, ECUs, etc.
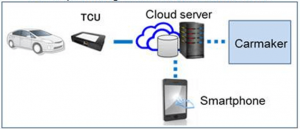
The TCU captures data from any ECU by simply listening in on the CAN-bus network. The sourced data is processed in the TCU for real-time applications such as tracking and diagnostics while non-real-time tasks such as weather information, traffic conditions, etc. are sent to the cloud for analysis. Data transfer to the cloud happens via reliable communication interfaces such as LTE, Wi-Fi, Bluetooth & Ethernet. This data is then made available to the user or third party via an application.
Core components of TCU
As with all embedded systems, The TCU comprises three core components:
Embedded Hardware:
For TCU hardware, ARM-based platforms are best, and preferably the ones having heterogeneous cores like NXP`s i.MX8 processors. These platforms are ideal for safety-certifiable and real-time performance requirements. The i.MX8 features an intelligent blend of MPUs+MCU power in a single chip. The MPU cores provide full 64-bit ARMv8-A support while the low-power microcontroller is ideal for critical real-time execution.
Embedded Software:
- Yocto based Linux kernel.
- FreeRTOS.
Communication interfaces/protocols:
The platform supports a wide range of wired /wireless communication interfaces, including:
- Ethernet, CAN, USB, UART, I2C
- Wi-Fi, Bluetooth Cellular network (2G/3G/4G, LTE)
- GPS/GNSS
Applications:
- Remote tracking
- Turn by turn navigation
- Route optimization
- eCall / bCall,
- Remote Doors
- Burglar Warning
- Speed Alert
- Fleet management
- Remote diagnosis
- Drowsiness detection
- Driver behavior
Key features of TCU
- Dual CAN interface for collecting the vehicle data and for vehicle diagnostics
- A global positioning system (GPS) unit, which keeps track of the latitude and longitude values of the vehicle
- Motion capture sensors – Accelerometer and Gyroscope and sensor to monitor the temperature of the engine
- External interface for mobile communication (LTE, Wi-Fi, Bluetooth & Ethernet)
- Inter core communication between MPU core and MCU core
With telematics increasingly becoming an integral part of the vehicle system, it is of utmost importance to select the right solution to ensure efficient and reliable operation. The key factors that need to be considered in a telematics system are:
1. Intelligent edge computing:
What enables intelligence at the edge? Real-time computing.
For a vehicle telematics system to be efficient, there needs to be a balance between real time computing in the vehicle and cloud-based data processing. What if there is a spark in the engine and the user is not warned on time? The result can be fatal. Real-time computation is very critical. But how can its efficiency be assured?
The computing platform chosen determines the real-time processing capability of a telematics system. A TCU system designed using NXP’s i.MX8 processors incorporate powerful ARM® Cortex® cores – Cortex® A35 MPU (runs Yocto Linux) & Cortex® M4 MCU (runs FreeRTOS).
The Cortex® M4 microcontroller is the key to real-time processing in the TCU.In case of an emergency, the M4 reacts immediately by informing the crisis to the A cores. The A core initiates immediate processing ,like activation of emergency call (eCall) services, inform exact condition ,location and passengers in the vehicle etc. This will allow emergency personnel to reach the vehicle quickly and with the right help. All other real time operations such as diagnostic data, tracking and navigation assistance, anti-theft alarm, etc. are monitored and managed efficiently by this power couple (Cortex® A35 & Cortex® M4).
2. Optimized Security:
Security is a huge challenge that need to be addressed strategically, step by step. A vehicle’s telematics system can easily become a target for cyber-attack, if not secured well enough with up-to-date, foolproof security mechanisms. At iWave, we have taken this challenge seriously.
We ensure all-round security in our platforms, starting from the chipset level with secured memory and trusted booting, and ensure the software launching on hardware is well protected through authentication and encryption mechanisms.
Security features in TCU solution:
- High Assurance Boot – HAB
- Encryption and Decryption using HW cryptography Engine
- Creation of Blob for protecting sensitive data
- Use of RPMB partition of eMMC for saving/accessing the sensitive data using a secure mechanism
For more details refer to our article on Security-Optimized Embedded Solutions:
3. Secure and reliable Over the Air Update (OTA)
With telematics applications evolving continuously, it is important to update the software running on the system with advanced features and security enhancements. But, how can this be done regularly and without human intervention? The answer is Over the Air Update (OTA).
iWave incorporates the OTA update solution using Mender open-source software update manager. To know more about it, check our article on iWave’s Expertise in Linux OTA (Over the Air) Update:
Software OTA in TCU solution:
- Multi-levels OTA guarantees future updates and robustness of TCU
- Supports both ‘managed mode’ (server will automatically take care of the updates) and ‘standalone mode’ (any third party software can decide when to update the system with or without network) updates
- Support for both application and system updates.
- No need for temporary storage for the update on the device.
iWave have the expertise to develop secure and reliable TCU solution build around iWave SOM or totally custom solution with our vast expertise in hardware and software embedded technologies.iWave’s OBD II is a turnkey telematics solution built completely in-house and has already conquered the market interest for its efficient performance in providing tracking and vehicle diagnostics data even in harsh environments such as heavy-duty mining vehicles.
To know more, write to us at mktg@iwavesystems.com or contact our regional partners.